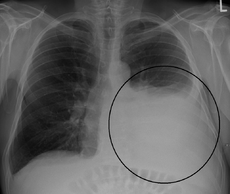
Pleural effusion is excess fluid that accumulates between the two pleural layers, the fluid-filled space that surrounds the lungs. Excessive amounts of such fluid can impair breathing by limiting the expansion of the lungs during ventilation.
Pathophysiology
Pleural fluid is secreted by the visceral layer of the pleura and reabsorbed by the parietal layer of the pleura.
Diagnosis
Pleural effusion is usually diagnosed on the basis of medical history and physical exam, and confirmed by chest x-ray. Once accumulated fluid is more than 300 ml, there are usually detectable clinical signs in the patient, such as decreased movement of the chest on the affected side, stony dullness to percussion over the fluid, diminished breath sounds on the affected side, decreased vocal resonance and fremitus (though this is an inconsistent and unreliable sign), and pleural friction rub. Above the effusion, where the lung is compressed, there may be bronchial breathing and egophony. In large effusion there may be tracheal deviation away from the effusion. A systematic review (2009) published as part of the Rational Clinical Examination Series in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) showed that dullness to conventional percussion was most accurate for diagnosing pleural effusion (summary positive likelihood ratio, 8.7; 95% confidence interval, 2.2–33.8), while the absence of reduced tactile vocal fremitus made pleural effusion less likely (negative likelihood ratio, 0.21; 95% confidence interval, 0.12–0.37).
Pathophysiology
Pleural fluid is secreted by the visceral layer of the pleura and reabsorbed by the parietal layer of the pleura.
Diagnosis
Pleural effusion is usually diagnosed on the basis of medical history and physical exam, and confirmed by chest x-ray. Once accumulated fluid is more than 300 ml, there are usually detectable clinical signs in the patient, such as decreased movement of the chest on the affected side, stony dullness to percussion over the fluid, diminished breath sounds on the affected side, decreased vocal resonance and fremitus (though this is an inconsistent and unreliable sign), and pleural friction rub. Above the effusion, where the lung is compressed, there may be bronchial breathing and egophony. In large effusion there may be tracheal deviation away from the effusion. A systematic review (2009) published as part of the Rational Clinical Examination Series in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) showed that dullness to conventional percussion was most accurate for diagnosing pleural effusion (summary positive likelihood ratio, 8.7; 95% confidence interval, 2.2–33.8), while the absence of reduced tactile vocal fremitus made pleural effusion less likely (negative likelihood ratio, 0.21; 95% confidence interval, 0.12–0.37).